Email Us : contact@sprginfotech.com
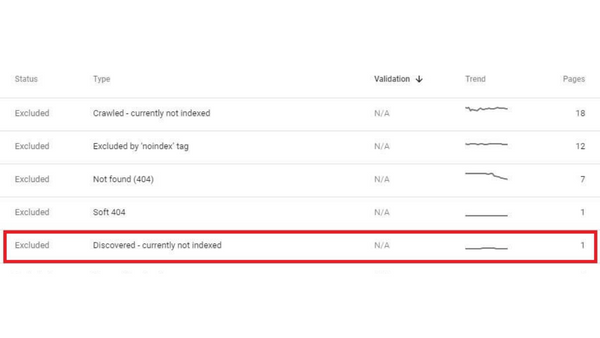
The term “Discovered currently not indexed” indicates that Google is aware of the URL but hasn’t crawled or indexed it. Using the five-step process to identify and solve the issue.
What is indexing a website?
Website indexation is the method used by search engines to include web material in their indexes. Search engines “crawl” websites in order to find pertinent keywords, metadata, and other signals that influence how and where content is ranked. Indexed websites must to have a content strategy that is easy to use, discoverable, and understandable.
How to Fix Discovered currently not indexed
- Check Backlinks
- Request indexing
- Check for crawl budget issue
- Check for content quality issue
- Check that content is internally linked
Check backlinks
One of the signs Google considers when determining whether a page is likely to be valuable and deserving of crawling are backlinks. If your page has no or few high-quality backlinks, Google may have “deprioritized” crawling as a result.
Getting more backlinks is undoubtedly the hardest task on the list, but it is valuable. Even one worthwhile connection can hasten Google’s discovery and indexing of your material.
Request indexing
Try requesting indexing through Google Search Console if you only notice a few pages with the “Discovered – presently not indexed” problem (GSC). To do so, select “URL inspection” from the menu and type the URL of the page. Click “Request indexing” if it isn’t already indexed.
If everything is in order, a message stating that the URL was placed to the priority crawl queue should display.
Before asking for indexing again if this doesn’t work, you nearly always need to identify and resolve an underlying problem.
Sending Google batch indexing queries is possible (i.e., multiple URLs at once).
Check for crawl budget issue
The crawl budget determines how quickly and how many pages of your website a search engine wants to crawl. You can notice the “Discovered – presently not indexed” warning if the number of crawlable URLs you have exceeds your crawl allowance.
Gary Illyes from Google claims that 90% of websites don’t need to be concerned. Although difficulties with crawl budgets typically affect larger sites, problems on smaller sites might arise from certain technical configurations, issues, and errors.
Let’s examine a few factors that can cause crawl budget problems and how to fix them.
Do you use subdomains to serve content?
Consider a scenario in which your primary website is located at example.com and your assets are located at cdn.example.com.
In this situation, the asset subdomain can be combined with your primary website and included in the crawl budget.
To fix this, think about providing resources via a CDN URL with a different crawl budget.
Do you frequently reroute traffic?
We usually add a redirect to another pertinent page when we decide to delete a page from the website. This isn’t always essential, though. It is preferable to remove or change internal links to the deleted page and return a 404, unless the page has backlinks or traffic.
Do you use redundant content?
If everything is in order, a message stating that the URL was placed to the priority crawl queue should display. Examples comprise:
- Both the www and non-www versions of your site, as well as HTTPS and HTTP, both lead to the same pages.
- instances for development or staging.
- Product or category pages that are empty or have generic content.
- Depending on your situation, there are different ways to handle duplicate content issues.
Have any internal nofollow links been used?
Nofollow links won’t stop an index from finding the page. Utilizing them internally, however, informs search engines that a page is not crucial.
Here’s how to identify nofollow internal links on pages for free:
- Examine your website with Site Audit
- Check out the Links report.
- Navigate to the “Issues” tab.
- Look for the notifications and warnings that state, “Page has nofollow incoming internal links only” and “Page has nofollow and do follow incoming internal links.”
Replace the nofollow links with followed ones if the page is significant.
What about orphan pages?
Google can discount your new page if the only method to find it is through the sitemap and it has no internal links.
Check for content quality issue
Not all of what Google finds is indexed. It places a strong value on original, interesting, and high-quality material.
Google cannot determine if the content is of low quality or not because it hasn’t yet crawled pages containing this warning. It may have “deprioritized” crawling since it may have an idea based on similar pages that it has already crawled.
Google is not likely to index certain types of material, including:
- Machine-translated material – If you localize information using Google’s Translate API or something similar, the translations won’t be perfect. If so, searchers won’t find it particularly helpful.
- Spun content is text that has been written by software. The end result is typically low-quality, copied information.
- AI-generated content – While AI writing tools are becoming more and more popular, they rarely produce insightful content on their own.
- Few innovative ideas can be found on pages with thin content.
In order to create something useful, thin content should either be eliminated or combined with additional thin stuff. If not, make the content better. Noindex the resulting material if it isn’t optimized for organic search so search engines can focus on crawling more significant pages.
Check that content is internally linked
Links within your website’s pages are known as internal links. URLs with few or no internal links are frequently viewed as irrelevant by Google, who may choose not to index them. You can check for free whether a URL contains internal links. This is how:
- Examine your website with Site Audit
- Activate the Page Explorer tool.
- Filter under “Content” for “All pages.”
- A column for “No. of all inlinks” should be included.
You might also be able to locate some orphan pages if you chose sitemaps and/or backlinks as your project’s URL sources.
To find the “Orphan page (has no inbound internal links)” error, simply access the Links report, choose the “Issues” option, and then scroll down.
With a crawling tool like Site Audit, it might not be possible to find every orphan page on your website. This is due to the lack of internal links on orphan pages.
It can also be used to look for opportunities for internal links between two already-existing pages. This is how:
- Go to the Site Audit’s Internal Link Opportunities report.
- The page to which you wish to add internal links and a term associated with it
- Select “Keyword” as your search option.
To locate possible pages to link from when publishing a new page, you may also search within the page text using Page Explorer.
But none of these strategies can take the place of a well-designed website with logical internal linkage. Every website should give that a high priority.
To “hack” your crawl depth and make sure all of your internal pages are linked from an HTML sitemap, nevertheless, is one solution if you’re having problems.
An HTML sitemap is a page that explains your website’s structure to visitors and makes it simpler for them to browse.
HTML sitemaps are designed for people, as opposed to XML sitemaps, which are created to be interpreted by various systems. Even though they’re occasionally regarded as obsolete, they remain important.
If your website is large, you might want to think about breaking it up into logical sections because you don’t want tens of thousands of URLs to be linked from a single page.
Use correct a> tags for internal links rather than JavaScript routines like onClick() to send users to different pages. They must be displayed as a> tags.
Why is Google not indexing my article?
Because we haven’t had a chance to crawl or index your new site or page, it may not yet be in our index. After you publish a new page, it takes some time until we crawl it, and even longer for us to index it.
What is an indexing error?
When your code encounters an index error, it signifies that it is attempting to access an erroneous index. The index generally exceeds its bounds because it is excessively large. An Index Error will appear, for instance, if you have a list with three items and attempt to access the fourth one.
How long does it take for Google to index?
Your new website will take 4 days to 4 weeks to be crawled and indexed by Google. However, this range is somewhat vast, and it has been disputed by those who assert to have scanned websites in fewer than 4 days.
Conclusion
Users should confirm their content is internally connected because Google may have “deprioritized” a page because it has few or no high-quality backlinks. Enter the page’s URL and select “URL inspection” from the menu to ask Google Search Console to index the page.
Machine-translated content, pages with little to no original content, and AI-generated content are some content categories that Google is not likely to index. Google typically considers URLs with few or no internal links to be irrelevant and may decide not to index them. You can use Site Audit and Page Explorer to detect orphan pages on your website. This is a result of orphan pages having no internal links.